

DATA AGGREGATED ACROSS 300 CRYPTO, 13 CRYPTO EXCHANGES, AND COUNTING AROUND THE GLOBE.














Beyond cross-exchange cryptocurrency arbitrage involving multiple exchanges, Sharkshimi covers other types of cryptocurrency arbitrage services. This includes: Triangular Crypto Arbitrage - to expand search for more profitable arbitrage opportunities to execute trades within a crypto exchange; Crypto Arbitrage Fee Calculator - to help calculate and visualize fees incurred from arbitrage trading to realize actual profitability; Crypto Wishlist - to keep track of cryptocurrencies that matter! Don't forget to follow us on X (@MattELabRND) to stay ahead of crypto arbitrage alerts!
Sharkshimi does not offer any paywall, subscription, tier-based, authentication, and authorization systems! All features built within Sharkshimi are made free and accessible to use with cross-platform support! Easily onboard with Sharkshimi's intuitive UIUX inspired from CoinGecko and CoinMarketCap!
Sharkshimi offers a customizable experience by auto saving data locally from where you left off; sorting and filtering table by crypto and crypto exchange; selecting preferred base currency; and toggling between dark and light mode!
Learn about cryptocurrency arbitrage!
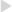
Crypto arbitrage is a trading strategy that takes advantage of price differences for the same cryptocurrency across different exchanges. Unlike traditional stocks—such as those traded on the NYSE or NASDAQ—where prices are consistent across platforms due to centralized order books, cryptocurrency markets are decentralized. Each crypto exchange (like Binance, Coinbase, or OKX) maintains its own independent order book. This means that the price of a cryptocurrency, such as Bitcoin or Ethereum, can vary from one platform to another depending on the local supply and demand on each exchange.
This price discrepancy creates an opportunity for arbitrage. For example, if Bitcoin is trading at a lower price on Exchange A (e.g., Binance) and at a higher price on Exchange B (e.g., Coinbase), a trader could:
- Buy Bitcoin on Exchange A at the lower price,
- Transfer the Bitcoin to Exchange B, and
- Sell it on Exchange B at the higher price.
Because the crypto market operates 24/7 and lacks a central price-setting mechanism, such arbitrage opportunities appear more frequently than in traditional finance—but they can also vanish quickly due to competition and market volatility.

An order book is a real-time list of all the buy and sell orders for a specific cryptocurrency trading pair, such as BTC/USD, on a particular exchange. It shows how much buyers are willing to pay (bids) and how much sellers are asking for (asks), along with the quantities they want to trade.
On the buy side (bids), traders place orders stating the maximum price they’re willing to pay for a certain amount of the crypto. On the sell side (asks), traders list the minimum price they’re willing to accept to sell their crypto.
For example, if someone wants to buy Bitcoin immediately, they can do so by accepting the lowest ask price currently listed. This is called "filling" an order. Likewise, if someone wants to sell their Bitcoin instantly, they can fill the highest bid price available.
In short, the order book reflects market supply and demand at various price levels, and it's how prices are determined on crypto exchanges in real time.

The bid-ask spread is the difference between the highest price a buyer is willing to pay for a cryptocurrency (the bid) and the lowest price a seller is willing to accept (the ask) on the order book.
For example, if the highest bid for Bitcoin is $30,000, and the lowest ask is $30,100, the bid-ask spread is $100.
This spread is important because it reflects the liquidity and trading activity of a market:
-A narrow spread (small difference) usually means there's high trading volume and strong competition between buyers and sellers.
-A wide spread often indicates low liquidity or less trading activity, which can make it more expensive to buy or sell instantly.
In short, the bid-ask spread is a key measure of how efficiently a crypto market operates.

Crypto trading—especially in strategies like arbitrage—involves frequent buying and selling. This can become expensive due to trading fees, particularly when using the taker fee model. A taker fee is charged when you fill an existing order in the order book (e.g., buying at the current lowest ask or selling at the highest bid). You're essentially "taking" liquidity from the market, and exchanges charge more for that convenience because the transaction is filled instantly.
However, exchanges want to encourage liquidity—the availability of orders in the market—because it results in a narrower bid-ask spread, meaning traders get better prices and faster fills overall. To promote this, they offer a lower maker fee to traders who place new orders (e.g., setting a buy order below the market price or a sell order above it). This is called "making" liquidity, as it adds to the order book rather than taking from it.
While maker fees are cheaper, the downside is that your order isn’t filled instantly—you’ll need to wait for a matching counter-order.

While on paper, a cryptocurrency arbitrage opportunity may seem profitable — such as buying a crypto asset at a lower price on Exchange A and selling it at a higher price on Exchange B — in reality, several technical and practical obstacles can make the trade unexecutable. One major reason is the issue of network compatibility during transfers.
To perform arbitrage, you often need to transfer the cryptocurrency from one exchange to another. This transfer happens on-chain, meaning it must be recorded and verified on a blockchain network (e.g., Ethereum, BNB Smart Chain, Solana, etc.). However, many cryptocurrencies exist on multiple networks — for example, USDT (Tether) can exist on Ethereum (ERC-20), Tron (TRC-20), Binance Smart Chain (BEP-20), and more.
The problem arises when the source exchange allows withdrawal on one network, and the target exchange only supports deposit on a different network. If a trader mistakenly sends crypto across incompatible networks, the funds can become irretrievable or "lost" unless customer support from both exchanges can manually recover it — a process that is time-consuming, uncertain, and sometimes not possible.

Triangular arbitrage is a trading strategy that involves exploiting price discrepancies between three different currencies or trading pairs within the same exchange or across multiple exchanges. It is called "triangular" because the trade forms a loop involving three steps — and three different currencies — that starts and ends with the same currency.
Here’s how it works:
- You begin with a certain amount of Currency A (for example, USDT).
- You use Currency A to buy Currency B (e.g., USDT → BTC).
- You then use Currency B to buy Currency C (e.g., BTC → ETH).
- Finally, you use Currency C to buy back Currency A (e.g., ETH → USDT).
If the exchange rates between these three pairs are misaligned — due to supply-demand imbalance, latency in price updates, or low liquidity — you may end up with more of Currency A than you started with, resulting in a risk-free profit before fees and slippage.
Learn about Sharkshimi!

Sharkshimi is a cryptocurrency arbitrage scanner. It extends features of crypto data aggregators (e.g., CoinGecko, CoinMarketCap, etc.), providing an intuitive user experience to help arbitrageurs identify real-time cross-exchange arbitrage opportunities from price discrepancies across crypto markets. All to help arbitrage traders facilitate automated trading!

 and
and  represent in the cross-exchange cryptocurrency arbitrage page within Sharkshimi?
represent in the cross-exchange cryptocurrency arbitrage page within Sharkshimi? (Bid): Highest price one is willing to buy a crypto for on a crypto exchange
(Bid): Highest price one is willing to buy a crypto for on a crypto exchange (Ask): Lowest price one is willing to sell a crypto for on a crypto exchange
(Ask): Lowest price one is willing to sell a crypto for on a crypto exchange

Arbitrage (%): Represents the maximum potential arbitrage return of a crypto across displayed crypto exchanges.
Formula (% Increase): [(Final Value - Initial Value) / Initial Value] X 100
Applied Formula (% Increase): [(Highest Bid Price Across Displayed Exchanges - Lowest Ask Price Across Displayed Exchanges) / Lowest Ask Price Across Displayed Exchanges] X 100
Formula Explanation:
Step 1 - Of all displayed crypto exchanges, find the exchange selling the least expensive crypto (e.g., Bitcoin) via the lowest ask price ( ) to buy from.
) to buy from.
Step 2 - Of all displayed crypto exchanges, find the exchange selling the most expensive Bitcoin via the highest bid price ( ) to sell to.
) to sell to.
Step 3 - Calculate the % increase using the lowest ask price ( ) which represents the crypto exchange to buy from as the initial value and the highest bid price (
) which represents the crypto exchange to buy from as the initial value and the highest bid price ( ) which represents the crypto exchange to sell to as the final value which represents the potential arbitrage return.
) which represents the crypto exchange to sell to as the final value which represents the potential arbitrage return.

Assuming you bought a crypto at a discount on exchange A for a trading fee of 1%, and trasferred the crypto to exchange B traded at a premium for a transfer fee of 1%, before finally selling the transferred crypto on exchange B for another trading fee of 1% to make an arbitrage profit. What is the total fee in % incurred?
If you answered 3% (1% Buy Fee + 1% Transfer Fee + 1% Sell Fee), it is incorrect. The answer is 2.9701% (1% Buy Fee + 1% of remaining 99% Transfer Fee + 1% of remaining 98.01% Sell Fee).
The cryptocurrency arbitrage fee calculator provides an accurate estimate of the total fee incurred from various types of transaction performed hypothetically during crypto arbitrage trading. It helps one understand the minimum Arbitrage (%) return to minimally break-even.

Sharkshimi supports over 300+ crypto and over 13+ crypto exchanges established across various regions of the world.

Sharkshimi supports over 200+ currencies in terms of currency exchange rate.

Sharkshimi is a responsive web app with official support across the following mobile devices:
- iPhone SE
- iPhone XR
- iPhone 12 Pro
- iPhone 14 Pro Max
- Pixel 7
- Samsung Galaxy S8+
- Samsung Galaxy S20 Ultra
- iPad Mini
- iPad Air
- iPad Pro

No. Sharkshimi does not require an account to access any of the available features. Only you have access to your data which is securely stored on your device.

Sharkshimi uses the most widely available base fiat currency or stablecoin within the API of the crypto exchange (i.e., either USD (United States Dollar), USDC (USD Coin) or USDT (Tether)) as the default base currency: Binance
 - USDT
- USDT Binance-US
 - USDT
- USDT Bitget
 - USDT
- USDT Bitstamp
 - USD
- USD Bybit
 - USDT
- USDT Coinbase
 - USDC
- USDC CryptoCom
 - USD
- USD Kraken
 - USD
- USD Kucoin
 - USDT
- USDT OKX
 - USDT
- USDT Upbit-Indonesia
 - USDT
- USDT Upbit-Singapore
 - SGD converted to USD via Google Finance
- SGD converted to USD via Google Finance Upbit-Thailand
 - USDT
- USDT